Buzzing with excitement, we delve into the fascinating world of bee communication: the waggle dance and beyond. 🐝🎶
Did you know that bees have their very own language? Just like humans, these incredible insects have developed a unique way of communicating with each other. It’s called the waggle dance, and it’s a language of movement that allows bees to share important information about food sources and nest locations. 🐝💃
So, how does this waggle dance work? Well, picture a bee boogieing on the honeycomb, wiggling and waggling with purpose. Through a series of precise steps and vibrations, the dancing bee indicates the direction and distance to a specific location. It’s like a secret dance code that other bees can decipher, ensuring the efficient coordination of their hive activities. How remarkable is that? 🕺💃
Join us on this bee-tastic journey as we explore the mysterious world of bee communication, unlocking the secrets of the waggle dance and discovering the amazing ways in which bees communicate beyond their sweet dance moves. Get ready to be amazed by the power of nature’s little dancers! 🐝🌟
Discover the captivating world of bee communication beyond the famous waggle dance. Bees have an intricate language that involves pheromones, vibrations, and even body language. Dive into the secrets of how bees communicate with each other, sharing vital information about food sources and nesting sites. Explore this enchanting aspect of the bee’s world and gain a deeper appreciation for their extraordinary communication abilities.
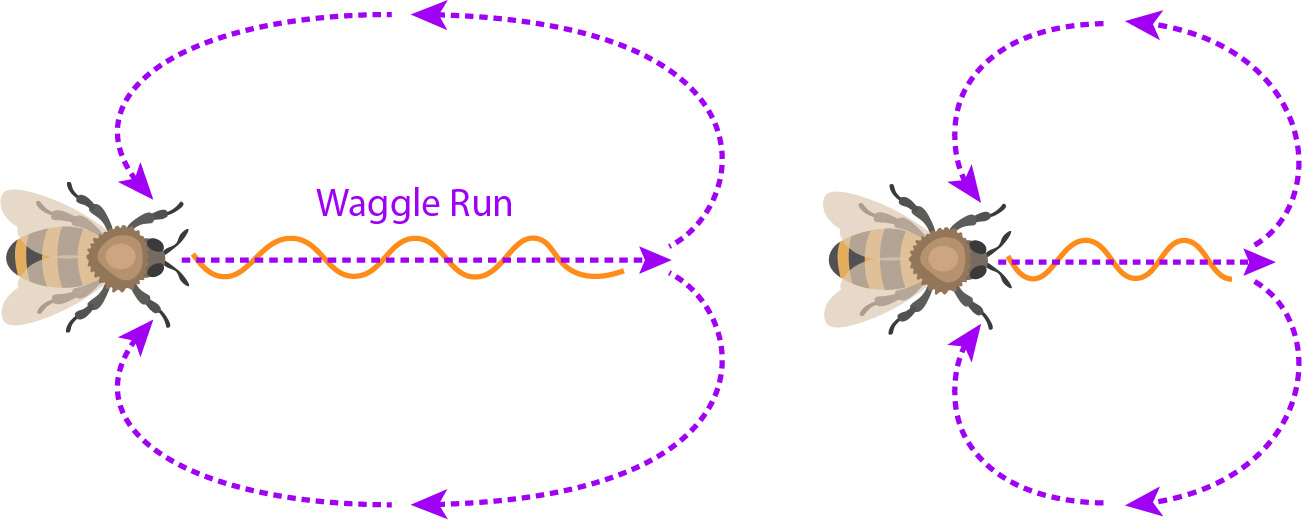
Bee Communication: The Waggle Dance and Beyond
Welcome to the fascinating world of bee communication! Bees are known for their intricate and sophisticated methods of communicating with each other. At the heart of their communication system lies the famous waggle dance, but there’s so much more to learn about how bees talk to one another. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of bee communication, exploring the waggle dance and other forms of bee language that contribute to their highly efficient and organized societies.
The Waggle Dance: A Language of Direction
The waggle dance is a remarkable behavior performed by worker bees to communicate the location of food sources, such as nectar or pollen, to their hive mates. This dance is a symbolic representation of a foraging bee’s flight pattern, and it provides precise information about the direction and distance of the food source, as well as its quality. Let’s take a closer look at how this incredible communication system works.
First, the forager bee returns to the hive after discovering a food source. It performs a series of waggle runs in a figure-eight pattern on the vertical surface of the honeycomb. The angle of the waggle run in relation to gravity indicates the direction of the food source in relation to the sun. For example, if the waggle run is performed upwards with an angle of 45 degrees to the left of gravity, it means that the food source is located 45 degrees to the left of the sun. The duration of the waggle run corresponds to the distance of the food source, with longer runs representing farther distances.
During the waggle dance, the forager bee can also communicate the quality of the food source through the duration and intensity of its waggle runs. If the food source is particularly abundant and of high quality, the bee will perform more vigorous and exaggerated waggle runs. This information helps other worker bees in the hive prioritize their foraging efforts and allocate their resources efficiently.
The Round Dance: A Universal Message
While the waggle dance is specialized for communicating distant food sources, bees also have a more generalized form of communication called the round dance. The round dance is used to convey information about nearby food sources that can be found within the immediate vicinity of the hive.
In contrast to the waggle dance, the round dance consists of circular movements on the honeycomb without any distinct orientation. By performing the round dance, the forager bee indicates to its nest mates that a food source is located nearby, but it does not give them any directional information.
Instead, the round dance relies on other sensory cues, such as the proximity of other bees and the scent of the food source, to guide the hive mates in finding the food. The round dance is a more generalized form of communication that can transmit information quickly and efficiently, especially when the food source is within a short distance from the hive.
Bee Communication: Vibrational Signals
While the waggle dance and the round dance are the most well-known forms of bee communication, bees also utilize vibrational signals to convey different messages within their colonies. These vibrational signals can be produced by various means, including drumming their abdomens against the honeycomb or shaking their wings in a specific pattern.
One example of vibrational communication is the “stop signal.” When a forager bee returns to the hive and encounters aggressive or dominant bees trying to steal its resources, it emits a vibrational signal that acts as a warning sign, instructing other bees to stop what they are doing and retreat.
Another example is the “worker piping signal,” which is produced by worker bees to indicate the need for a new queen in the colony. This signal is used when the existing queen is aging or has died, and it triggers the production of new queen bees by the worker bees.
Bee Communication: Chemical Signals
In addition to visual and vibrational communication, bees also use chemical signals known as pheromones to convey messages within their colonies. Pheromones are chemical substances that can trigger specific behaviors or responses in other members of the same species.
One important pheromone used by bees is the “alarm pheromone.” When a bee feels threatened or attacked, it releases this pheromone to alert other bees of the danger. The alarm pheromone acts as a signal for other bees to be on high alert and to take defensive actions to protect the hive.
Bees also use pheromones for various other purposes, such as marking food sources, attracting mates, and maintaining social cohesion within the hive. These chemical signals play a crucial role in coordinating the complex activities and behaviors of the bee colony.
Bee Communication: The Language of Survival
Bee communication is a remarkable example of how animals have evolved complex and sophisticated systems to interact and coordinate their activities. Through the waggle dance, the round dance, vibrational signals, and chemical messages, bees are able to effectively communicate vital information about food sources, threats, and the needs of the colony.
Studying bee communication not only provides insight into the fascinating world of bees but also offers valuable lessons in teamwork, organization, and efficient resource allocation. By understanding the language of bees, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the incredible diversity of communication systems found in the natural world.
Protecting Bee Communication: The Role of Conservation
As we learn more about the intricacies of bee communication, it becomes clear that protecting bee populations is crucial for maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystems. Bees play a vital role in pollination, which is essential for the reproduction of many plant species and the production of food crops that humans rely on.
One of the biggest threats to bees is habitat loss and the use of pesticides, which can disrupt their communication systems and lead to declines in their populations. As individuals, we can contribute to bee conservation by planting native, bee-friendly plants in our gardens, avoiding the use of pesticides, and supporting organizations and initiatives dedicated to protecting bees and their habitats.
The Future of Bee Communication Research
Bee communication continues to be a field of ongoing research and discovery. Scientists are continually uncovering new aspects of bee language and exploring the intricacies of their communication systems.
Advancements in technology, such as high-speed cameras and sophisticated sensors, allow researchers to capture and analyze the complex behaviors and signals of bees in greater detail than ever before. These advancements enable us to unravel the mysteries of bee communication and gain valuable insights into how these remarkable creatures interact and communicate with each other.
Conclusion
Bee communication is a captivating subject that highlights the complexity and richness of the natural world. From the waggle dance to the round dance, vibrational signals, and chemical messages, bees have developed a vast repertoire of communication methods to ensure the survival and success of their colonies.
Understanding and appreciating bee communication not only deepens our knowledge of these incredible insects but also emphasizes the importance of protecting and conserving their habitats. By taking action to promote bee conservation, we can help safeguard the future of these remarkable creatures and the essential role they play in our ecosystems.
Key Takeaways: Bee Communication: The Waggle Dance and Beyond
- The waggle dance is a unique form of bee communication where bees waggle and circle to indicate the direction and distance of food sources.
- Bees also communicate through pheromones, releasing chemicals to convey messages about food availability, danger, and the location of their hive.
- The waggle dance and pheromone communication help bees work together as a colony and efficiently gather nectar and pollen.
- Scientists have found that bees can learn and remember complex communication patterns, demonstrating their remarkable intelligence.
- Understanding bee communication is crucial for studying and conserving these important pollinators, as it helps us comprehend their behavior and needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Wondering about how bees communicate and the fascinating waggle dance? Look no further! We’ve got the answers to your burning questions about bee communication and beyond.
How do bees communicate through the waggle dance?
The waggle dance is an intricate form of communication used by honeybees to convey important information about food sources to their fellow hive members. Essentially, when a bee discovers a good food source, it returns to the hive and performs a dance. By waggling its body and shaking its abdomen, the bee communicates the direction, distance, and quality of the food source to its hive mates.
The direction is indicated by the angle of the waggle dance in relation to the sun, while the honeybee’s body movement represents the distance relative to the length of the waggle run. The intensity and duration of the waggle dance also provide information about the quality of the food source, with longer and more vigorous dances indicating better resources.
What are other ways bees communicate besides the waggle dance?
While the waggle dance is a well-known form of communication among honeybees, it is not the only method they use to convey messages. Bees also communicate through scent, vibrations, and touch. For example, bees release pheromones or chemical scents to mark their territories or attract other bees to food sources.
Vibrations are another important means of communication. Bees create vibrations by rapidly vibrating their wings or tapping their bodies against the surface of the hive. These vibrations can signal danger, such as the presence of predators, or communicate the need for more resources within the hive.
How do bees learn the waggle dance?
The waggle dance is not an innate behavior in bees. Instead, it is learned and passed down through generations. Young worker bees observe and learn the waggle dance from experienced foragers. They watch the dance, learn the specific movements, and eventually perform it themselves when they become foragers.
Through this observational learning process, young bees acquire the skills to communicate the location of food sources to their hive mates. This cultural transmission of the waggle dance ensures that vital information is consistently shared within the bee colony and enables efficient foraging for resources.
What happens if the waggle dance isn’t accurate?
The accuracy of the waggle dance is crucial for the success of foraging honeybees. If the information conveyed through the waggle dance is inaccurate, it can lead other bees in the hive to waste time and energy searching for nonexistent food sources or become confused.
However, honeybees have mechanisms in place to ensure the accuracy of the waggle dance. They rely on multiple bees to confirm and cross-reference the information provided by the waggle dance. Additionally, bees continuously update their knowledge of food sources, adjusting their dances based on the changing availability and quality of resources.
Do all bee species use the waggle dance?
No, not all bee species use the waggle dance as a means of communication. The waggle dance is primarily used by honeybees, specifically the Western honeybee (Apis mellifera). It is a highly evolved form of communication that allows honeybees to share crucial information about food sources and contribute to the overall efficiency and success of the hive.
Other bee species often use different communication methods, such as pheromones or simple physical contact, to convey information within their colonies. Each bee species has its unique set of communication strategies that are adapted to their specific needs and environment.
The Waggle Dance | Inside the Animal Mind | BBC
Summary
Bees can communicate with each other using the waggle dance and other signals. The waggle dance tells other bees where to find food and how far away it is. Bees also use pheromones to leave scent trails for other bees to follow. This helps them navigate and find their way back to the hive. Bee communication is a fascinating way for these tiny insects to share information and work together as a team.
Leave a comment