Did you know that bees, those tiny creatures buzzing around flowers, have genders too? That’s right! Just like humans and other animals, bees have males and females. But have you ever wondered what determines the gender of a bee? In this article, we’ll dive into the fascinating world of bees and uncover the secrets behind their gender determination.
So, what determines the gender of a bee? Well, it all starts with the queen bee. She is the ruler of the hive and holds the key to determining the gender of her offspring. The queen bee has the ability to decide whether she wants to lay eggs that will become female worker bees or eggs that will develop into male drones.
But how does the queen bee make this decision? It all boils down to what she feeds the larvae. The queen bee secretes a special substance called royal jelly, which she feeds to certain larvae, and this determines their future gender. Larvae that are fed royal jelly will develop into female worker bees, while those that are not will become male drones.
Now that we know the basics of how bees determine their gender, let’s explore this fascinating process in more detail. Join us on this journey to discover the intricate world of bees and uncover the mysteries of what determines the gender of these incredible creatures. Get ready to dive into a world buzzing with excitement!
What Determines the Gender of a Bee?
In the enchanting world of bees, there is a fascinating process that determines their gender. From worker bees to queens and drones, understanding what determines the gender of a bee can help us appreciate the intricate workings of these buzzing creatures. In this article, we will dive into the intricate world of bees and explore the factors that influence their gender.
The Role of Genetics in Bee Gender
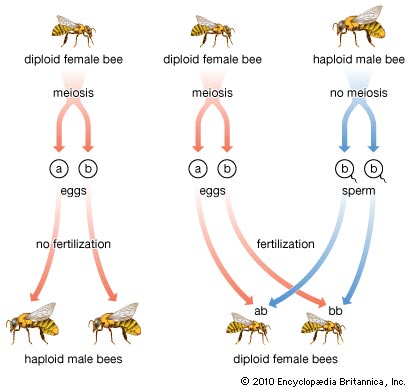
Genetics play a crucial role in determining the gender of bees. Bees have a haplodiploid system of sex determination, which means that their gender is determined by the number of chromosomes they inherit from their parents. Female bees, including queens and workers, are diploid, meaning they inherit two sets of chromosomes from their parents. Male bees, known as drones, are haploid, meaning they inherit only one set of chromosomes.
The female bees are produced through fertilized eggs, where the queen bee contributes both the egg and sperm. However, male bees are the product of unfertilized eggs, where the queen bee lays an egg without fertilization. This egg, containing only the queen’s genetic material, will develop into a male bee. The mechanism by which this happens is still a topic of scientific research and intrigue.
Genetic variation is vital for the survival of bee colonies. The drones, being haploid, have the potential to introduce new genetic material into the bee population through mating with queens from other colonies. This genetic diversity helps maintain the overall health and adaptability of the collective bee population.
Environmental Factors Impacting Bee Gender
While genetics play a significant role in determining bee gender, various environmental factors can also have an influence. One such factor is the nutrition provided to the developing larvae. The food that larvae receive during their early stages of development can affect their gender.
The diet of the larvae is regulated by the worker bees. In general, worker bees’ diet is primarily composed of pollen and nectar. However, when the colony needs more worker bees, the diet of the larvae is adjusted to promote the development of females. Conversely, when the colony requires drones, the diet of the larvae is altered, resulting in the development of male bees.
Another environmental factor that can impact bee gender is temperature. Researchers have found that temperature can influence the development of male bees. Warmer temperatures promote the production of drones, while cooler temperatures can lead to the production of females. This temperature-dependent process adds another layer of complexity to the gender determination of bees.
The Queen Bee’s Role in Gender Determination
The queen bee, as the sole fertile female in the colony, holds significant sway in determining the gender of the offspring. While the queen contributes the same number of chromosomes to all her eggs, the process of fertilization or lack thereof determines whether the offspring will be male or female.
During mating, the queen bee stores the sperm from multiple drones in a specialized organ called the spermatheca. Each time the queen lays an egg, she can selectively release sperm, depending on the type of bee she wants to produce. If she wants to lay a fertilized egg and produce a female worker bee or queen, she releases the stored sperm. If she wants to lay an unfertilized egg and produce a male drone, she refrains from releasing stored sperm.
The queen’s ability to selectively control the gender of her offspring is remarkable and provides her with the means to regulate the colony’s composition based on its needs. This ability to manipulate the gender of the next generation adds an element of flexibility and adaptability to the bee colony’s survival strategies.
Implications and Significance
Understanding what determines the gender of a bee provides us with a deeper appreciation for the complexity and sophistication of these buzzing creatures. While genetics play a fundamental role, environmental factors and the queen bee’s influence shape the gender composition of a bee colony.
This knowledge can have important implications for beekeeping practices and conservation efforts. By understanding the factors that influence bee gender, beekeepers can make informed decisions to promote the health and success of their colonies. Conservationists can also use this knowledge to create environments that support the diverse gender composition necessary for the bees’ survival and genetic diversity.
So, the next time you spot a bee buzzing past, take a moment to appreciate the intricacies of its gender determination and the vital role it plays in the world of bees. There is so much more to these extraordinary insects than meets the eye.
Key Takeaways: What determines the gender of a bee?
- Bees have a unique gender determination system called haplodiploidy.
- Females develop from fertilized eggs and males develop from unfertilized eggs.
- The number of chromosomes in the egg determines the gender of the bee.
- The queen bee controls the gender of the colony by selectively laying fertilized or unfertilized eggs.
- Environmental factors can also influence the gender of bees, such as temperature and nutrition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our FAQ section on what determines the gender of a bee! Here, we’ll unravel the mysteries behind the fascinating world of bee biology and reproduction. Read on to find answers to commonly asked questions about bee genders.
1. How are bees born male or female?
Bees are fascinating creatures when it comes to determining their gender. The gender of bees is determined by the queen bee. The queen bee is the only fertile female in the entire colony and has the ability to produce both male and female offspring. When the queen bee mates with a drone bee, the resulting fertilized eggs develop into female worker bees. On the other hand, unfertilized eggs laid by the queen bee will become male bees, known as drones. So, it is the act of fertilization that determines the gender of a bee.
It’s important to note that drones have half the number of chromosomes as female bees. While female bees have two copies of each chromosome, drones only have a single copy. This haploid nature of drones makes them genetically distinct from female worker bees.
2. How does the queen bee choose the gender of her offspring?
The queen bee indirectly chooses the gender of her offspring through a process called “haplodiploidy.” In haplodiploid species like bees, females are diploid, meaning they have two sets of chromosomes, while males are haploid, with only one set of chromosomes. When the queen bee mates, she stores the sperm from the drone bee in her spermatheca, a special organ in her abdomen.
When the queen bee lays an egg, she can choose whether or not to fertilize it by releasing stored sperm. Fertilized eggs develop into female worker bees, while unfertilized eggs become male bees. By controlling whether or not she fertilizes an egg, the queen bee indirectly determines the gender of her offspring, ensuring a balanced ratio of males and females within the hive.
3. Are all worker bees female?
Yes, all worker bees in a honeybee colony are female. Worker bees are non-reproductive females who perform various tasks within the hive, such as gathering nectar, building and maintaining the hive, tending to the queen and larvae, and defending the colony from intruders. These hardworking females are essential for the survival and functioning of the entire bee colony.
Worker bees undergo different developmental stages, starting as eggs and progressing through larval and pupal stages before emerging as fully developed adult bees. The development of a female worker bee is influenced by various factors, including nutrition, pheromones, and environmental cues, all regulated by the queen bee.
4. What is the role of male bees in a colony?
Male bees, known as drones, have a critical but limited role in a bee colony. Drones do not have the physical capabilities to gather nectar or pollen, nor do they contribute to the hive’s daily work. Their primary purpose is to mate with queen bees from other colonies. Drones are larger in size than worker bees and have larger eyes, allowing them to spot potential mates in flight.
Once a drone successfully mates with a queen bee, its life’s purpose is fulfilled. Sadly, drones die shortly after mating, as their reproductive organs are torn away during the act. However, during mating season, drones play a crucial role in maintaining genetic diversity within bee populations and facilitating the reproduction of honeybee colonies.
5. Can bees change their gender?
Bees do not have the capability to change their gender. Once an egg is laid, it is determined whether it will become a female worker bee or a male drone bee. The gender of a bee is solely determined by whether or not the egg is fertilized by the queen bee’s stored sperm. Once this determination is made, it remains fixed throughout the bee’s life cycle.
However, it’s interesting to note that during times of extreme stress or when there is a lack of reproductive opportunities, worker bees can lay unfertilized eggs. These unfertilized eggs, though, will only develop into male drone bees. This behavior, known as “thelytoky,” is a rare exception to the usual process of gender determination in bees.
Sex Determination in Honey Bees | Principles of Inheritance | Biology | Khan Academy
Summary
So, what determines the gender of a bee? It turns out that bees have a unique system called haplodiploidy, where males develop from unfertilized eggs and females develop from fertilized eggs. The queen bee controls the gender by selectively fertilizing certain eggs.
Additionally, the worker bees, who are all female, play a crucial role in determining the gender of the new bees. They have the power to manipulate food resources and can influence whether an egg becomes a female worker bee or a male drone bee. This complex system ensures the survival and success of the bee colony.
Leave a comment